クイック スタート
This guide will step you through the process of creating a barebones Hello World app in Electron, similar to electron/electron-quick-start.
このチュートリアルを終えると、ブラウザウインドウを開いて Chromium、Node.js、Electron それぞれの実行バージョン情報のウェブページを表示できるアプリが完成します。
必要な環境
Electron を使用するには、 Node.js をインストールする必要があります。 利用可能な最新の LTS バージョンのインストールを推奨します。
お使いのプラットフォーム向けのビルド済みインストーラを使用して、Node.js をインストールするようにしてください。 さもなくば、他の開発ツールと互換性の問題が発生することがあります。
Node.js が正しくインストールされたかどうかを確認するため、お使いのターミナルクライアントで以下のコマンドを入力してください。
node -v
npm -v
このコマンドで、Node.js と npm のバージョンが表示されている必要があります。
注意: Electron は Node.js をバイナリに組み込んでいるため、コードを実行している Node.js のバージョンとシステムが実行しているバージョンは関係ありません。
アプリケーションを作成する
プロジェクトの雛形を作る
Electron アプリは、他の Node.js プロジェクトと同様の一般的な構造に従います。 まず、フォルダを作成し npm パッケージを初期化します。
- npm
- Yarn
mkdir my-electron-app && cd my-electron-app
npm init
mkdir my-electron-app && cd my-electron-app
yarn init
このインタラクティブな init コマンドでは、設定でいくつかフィールドの入力を促されます。 このチュートリアルの目的上、以下のルールに従ってください。
entry pointはmain.jsでなければなりません。authorとdescriptionはどのような値でも構いませんが、アプリのパッケージ化 で必要になります。
package.json ファイルは、以下のようになっていなければなりません。
{
"name": "my-electron-app",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "Hello World!",
"main": "main.js",
"author": "Jane Doe",
"license": "MIT"
}
そして、アプリの devDependencies に electron パッケージインストールします。
- npm
- Yarn
npm install --save-dev electron
yarn add --dev electron
Note: If you're encountering any issues with installing Electron, please refer to the Advanced Installation guide.
最後に、Electron を実行できるようにしたいと思います。 package.json の設定の scripts フィールドに、以下のような start コマンドを追加します。
{
"scripts": {
"start": "electron ."
}
}
この start コマンドにより、アプリを開発モードで開けます。
- npm
- Yarn
npm start
yarn start
注: このスクリプトは、Electron をプロジェクトのルートフォルダで実行するように指示しています。 今の段階のアプリでは、実行するアプリが見つからないというエラーが出ます。
メインプロセスを実行する
Electron アプリケーションのエントリポイントは、main スクリプトです。 このスクリプトは、メインプロセス を制御します。メインプロセスは完全な Node.js 環境で実行され、アプリのライフサイクルの制御、ネイティブインターフェースの表示、特権的操作の実行、レンダラープロセスの管理などを行います (詳細は後述)。
実行時、Electron はこのスクリプトをアプリの package.json の設定にある main フィールドから探します。これは プロジェクトの雛形を作る ステップで設定してあるはずです。
main スクリプトを書き始めるにあたって、プロジェクトのルートフォルダに main.js という空のファイルを作成します。
注: この時点で
startスクリプトを再度実行すると、アプリはエラーを出さなくなります。 しかし、main.jsにコードを追加していないためまだ何もしません。
ウェブページの作成
アプリケーションのウインドウを作成する前に、ウインドウが読み込むコンテンツを作成する必要があります。 Electron では、各ウィンドウがローカル HTML ファイルまたはリモート URL から読み込んだウェブコンテンツを表示します。
このチュートリアルでは、前者を行います。 プロジェクトのルートフォルダに以下の index.html ファイルを作成しましょう。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<!-- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/CSP -->
<meta http-equiv="Content-Security-Policy" content="default-src 'self'; script-src 'self'">
<title>Hello World!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
We are using Node.js <span id="node-version"></span>,
Chromium <span id="chrome-version"></span>,
and Electron <span id="electron-version"></span>.
</body>
</html>
注: この HTML ドキュメントを見ると、バージョン番号が本文から抜けていることがわかります。 これは JavaScript で後から手動挿入します。
ブラウザウインドウでウェブページを開く
ウェブページができたので、これをアプリケーションウインドウに読み込ませます。 そのためには、以下 2 つの Electron モジュールが必要です。
- The
appmodule, which controls your application's event lifecycle. - The
BrowserWindowmodule, which creates and manages application windows.
メインプロセスは Node.js で動作するので、これらを CommonJS モジュールとして main.js ファイルの先頭でインポートします。
const { app, BrowserWindow } = require('electron')
次に、createWindow() 関数を追加し、そこで index.html を新規作成した BrowserWindow インスタンスに読み込ませます。
const createWindow = () => {
const win = new BrowserWindow({
width: 800,
height: 600
})
win.loadFile('index.html')
}
次に、この createWindow() 関数を呼び出してウインドウを開きます。
In Electron, browser windows can only be created after the app module's ready event is fired. You can wait for this event by using the app.whenReady() API. whenReady() が Promise を解決した後、それが createWindow() を呼び出します。
app.whenReady().then(() => {
createWindow()
})
注: この時点で、Electron アプリケーションはウェブページを表示するウィンドウを開くことに成功しているはずです。
ウインドウのライフサイクルを管理する
ブラウザウインドウを開くことができるようになりましたが、各プラットフォームでよりネイティブな感じを出すためには、いくつか追加の雛形コードが必要です。 アプリケーションウィンドウは OS ごとに異なる動作をしますが、Electron はこれらの規則をアプリに実装する責任を開発者負担にしています。
一般的には、process グローバルの platform 属性を使用して、特定のオペレーティングシステム専用のコードを実行できます。
全ウインドウを閉じた時にアプリを終了する (Windows & Linux)
一般的に Windows や Linux では、すべてのウィンドウを終了するとアプリケーションが完全に終了します。
To implement this, listen for the app module's 'window-all-closed' event, and call app.quit() if the user is not on macOS (darwin).
app.on('window-all-closed', () => {
if (process.platform !== 'darwin') app.quit()
})
開いたウインドウがない場合にウインドウを開く (macOS)
Linux や Windows のアプリはウインドウを開いていないと終了してしまいますが、macOS のアプリは一般的にウインドウを開いていなくても起動し続け、ウインドウがないときにアプリをアクティブにすると新規ウインドウが開きます。
To implement this feature, listen for the app module's activate event, and call your existing createWindow() method if no browser windows are open.
ready イベントの前ではウインドウを作成できないので、アプリが初期化された後に activate イベントだけをリッスンする必要があります。 そのためには、既存の whenReady() コールバックの中で、イベントリスナーをアタッチします。
app.whenReady().then(() => {
createWindow()
app.on('activate', () => {
if (BrowserWindow.getAllWindows().length === 0) createWindow()
})
})
注: この時点で、ウインドウのコントロールが完全に機能しているはずです。
プリロードスクリプトを使ってレンダラーから Node.js にアクセスする
さて、最後にやるべきことは Electron とその依存関係のバージョン番号をウェブページに出力することです。
この情報へアクセスするには、Node のグローバルである process オブジェクトを介してメインプロセスで行うのが簡単です。 しかし、メインプロセスはレンダラーの document コンテキストにアクセスできないため、メインプロセスから DOM を編集できません。 これらは全く別のプロセスだからです!
Note: If you need a more in-depth look at Electron processes, see the Process Model document.
そこで、プリロード スクリプトをレンダラーにアタッチすると便利です。 プリロードスクリプトは、レンダラープロセスが読み込まれる前に実行され、レンダラーのグローバル (window や document など) と Node.js 環境の両方にアクセスできます。
preload.js という名前の新規スクリプトを以下のように作成します。
window.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', () => {
const replaceText = (selector, text) => {
const element = document.getElementById(selector)
if (element) element.innerText = text
}
for (const dependency of ['chrome', 'node', 'electron']) {
replaceText(`${dependency}-version`, process.versions[dependency])
}
})
上記のコードでは、Node.js の process.versions オブジェクトにアクセスし、基本的な replaceText ヘルパー関数を実行して HTML ドキュメントにバージョン番号を挿入しています。
このスクリプトをレンダラープロセスにアタッチするには、既存の BrowserWindow コンストラクタの webPreferences.preload 引数にプリロードスクリプトへのパスを渡します。
const { app, BrowserWindow } = require('electron')
// ファイルの先頭で Node.js の 'path' モジュールをインクルードします。
const path = require('node:path')
// 既存の createWindow() 関数を書き換えましょう
const createWindow = () => {
const win = new BrowserWindow({
width: 800,
height: 600,
webPreferences: {
preload: path.join(__dirname, 'preload.js')
}
})
win.loadFile('index.html')
}
// ...
ここでは、以下 2 つの Node.js のコンセプトが使われています。
__dirname文字列は、現在実行中のスクリプトのパス (ここではプロジェクトのルートフォルダ) を指しています。path.joinAPI は、複数のパス断片を結合し、すべてのプラットフォームで動作する結合パス文字列を作成します。
現在実行中の JavaScript ファイルからの相対パスを使用しているので、開発モードとパッケージモードの両方で相対パスが機能します。
おまけ: ウェブコンテンツに機能を追加する
この時点で、アプリケーションに機能を追加するにはどうしたらよいかと思われるかもしれません。
ウェブコンテンツとやり取りする場合は、レンダラープロセスにスクリプトを追加する必要があります。 なぜならレンダラは通常のウェブ環境で動作するので、<script> タグを index.html ファイルの最後の </body> タグの直前に追加して任意のスクリプトをインクルードできます。
<script src="./renderer.js"></script>
renderer.js に含まれるコードは、webpack でコードをバンドルして最小化したり、React を使用してユーザーインターフェースを管理するなど、一般的なフロントエンド開発と同じ JavaScript API やツールを利用できます。
まとめ
以上の手順により、以下のような完全な機能の Electron のアプリケーションが完成しました。
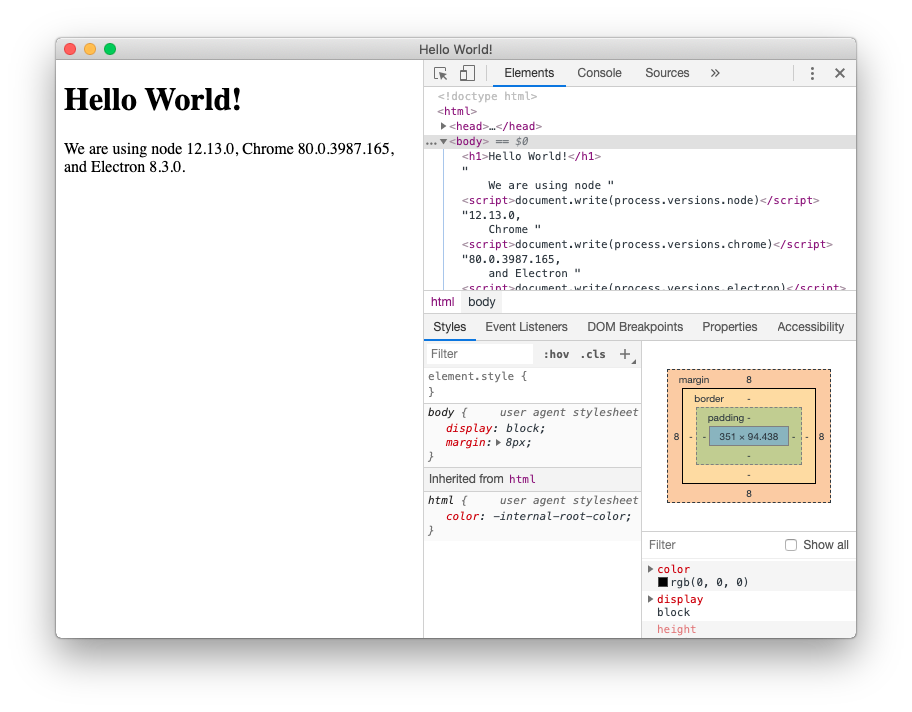
コード全体は以下のとおりです。
// main.js
// このモジュールはアプリケーションの生き死にを制御し、ネイティブブラウザウインドウを作成します
const { app, BrowserWindow } = require('electron')
const path = require('node:path')
const createWindow = () => {
// ブラウザウインドウを作成します。
const mainWindow = new BrowserWindow({
width: 800,
height: 600,
webPreferences: {
preload: path.join(__dirname, 'preload.js')
}
})
// そしてアプリの index.html を読み込みます。
mainWindow.loadFile('index.html')
// デベロッパー ツールを開きます。
// mainWindow.webContents.openDevTools()
}
// このメソッドは、Electron の初期化が完了し、
// ブラウザウインドウの作成準備ができたときに呼ばれます。
// 一部のAPIはこのイベントが発生した後にのみ利用できます。
app.whenReady().then(() => {
createWindow()
app.on('activate', () => {
// macOS では、Dock アイコンのクリック時に他に開いているウインドウがない
// 場合、アプリのウインドウを再作成するのが一般的です。
if (BrowserWindow.getAllWindows().length === 0) createWindow()
})
})
// macOS を除き、全ウインドウが閉じられたときに終了します。 ユーザーが
// Cmd + Q で明示的に終了するまで、アプリケーションとそのメニューバーを
// アクティブにするのが一般的です。
app.on('window-all-closed', () => {
if (process.platform !== 'darwin') app.quit()
})
// このファイルでは、アプリ内のとある他のメインプロセスコードを
// インクルードできます。
// 別々のファイルに分割してここで require することもできます。
// preload.js
// プリロードプロセスでは Node.js の全 API が利用可能です。
// Chrome 拡張機能と同じサンドボックスも持っています。
window.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', () => {
const replaceText = (selector, text) => {
const element = document.getElementById(selector)
if (element) element.innerText = text
}
for (const dependency of ['chrome', 'node', 'electron']) {
replaceText(`${dependency}-version`, process.versions[dependency])
}
})
<!--index.html-->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<!-- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/CSP -->
<meta http-equiv="Content-Security-Policy" content="default-src 'self'; script-src 'self'">
<title>Hello World!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
We are using Node.js <span id="node-version"></span>,
Chromium <span id="chrome-version"></span>,
and Electron <span id="electron-version"></span>.
<!-- このプロセスで他ファイルを require して実行することもできます -->
<script src="./renderer.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
- main.js
- preload.js
- index.html
const { app, BrowserWindow } = require('electron/main')
const path = require('node:path')
function createWindow () {
const win = new BrowserWindow({
width: 800,
height: 600,
webPreferences: {
preload: path.join(__dirname, 'preload.js')
}
})
win.loadFile('index.html')
}
app.whenReady().then(() => {
createWindow()
app.on('activate', () => {
if (BrowserWindow.getAllWindows().length === 0) {
createWindow()
}
})
})
app.on('window-all-closed', () => {
if (process.platform !== 'darwin') {
app.quit()
}
})
window.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', () => {
const replaceText = (selector, text) => {
const element = document.getElementById(selector)
if (element) element.innerText = text
}
for (const type of ['chrome', 'node', 'electron']) {
replaceText(`${type}-version`, process.versions[type])
}
})
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Hello World!</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Security-Policy" content="script-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline';" />
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
<p>
We are using Node.js <span id="node-version"></span>,
Chromium <span id="chrome-version"></span>,
and Electron <span id="electron-version"></span>.
</p>
</body>
</html>
これまでのステップを以下にまとめます。
-
Node.js アプリケーションを立ち上げ、Electron を依存関係に追加しました。
-
アプリ制御を担うメインプロセスを実行する
main.jsスクリプトを作成し、Node.js 環境で動作させました。 このスクリプトでは、Electron のappとBrowserWindowモジュールを使って、ウェブコンテンツを別のプロセス (レンダラー) で表示するブラウザウインドウを作成しました。 -
レンダラーで特定の Node.js の機能にアクセスするために、
BrowserWindowのコンストラクタでプリロードスクリプトをアタッチしました。
アプリケーションのパッケージと頒布
できたてのアプリを頒布する最速手段は Electron Forge を利用する方法です。
Linux 向けの RPM パッケージを構築するには、必要なシステムの依存関係をインストールする 必要があります。
-
package.jsonファイルに説明を追加します。さもなくば、rpmbuild が失敗します。 空の説明は無効です。 -
アプリの開発用依存関係に Electron Forge を追加し、その
importコマンドで Forge のセットアップをします。- npm
- Yarn
npm install --save-dev @electron-forge/cli
npx electron-forge import
✔ Checking your system
✔ Initializing Git Repository
✔ Writing modified package.json file
✔ Installing dependencies
✔ Writing modified package.json file
✔ Fixing .gitignore
We have ATTEMPTED to convert your app to be in a format that electron-forge understands.
Thanks for using "electron-forge"!!!npm install --save-dev @electron-forge/cli
yarn dlx electron-forge import
✔ Checking your system
✔ Initializing Git Repository
✔ Writing modified package.json file
✔ Installing dependencies
✔ Writing modified package.json file
✔ Fixing .gitignore
We have ATTEMPTED to convert your app to be in a format that electron-forge understands.
Thanks for using "electron-forge"!!! -
以下のように Forge の
makeコマンドで頒布形式を作成します。- npm
- Yarn
npm run make
> my-electron-app@1.0.0 make /my-electron-app
> electron-forge make
✔ Checking your system
✔ Resolving Forge Config
We need to package your application before we can make it
✔ Preparing to Package Application for arch: x64
✔ Preparing native dependencies
✔ Packaging Application
Making for the following targets: zip
✔ Making for target: zip - On platform: darwin - For arch: x64yarn make
> my-electron-app@1.0.0 make /my-electron-app
> electron-forge make
✔ Checking your system
✔ Resolving Forge Config
We need to package your application before we can make it
✔ Preparing to Package Application for arch: x64
✔ Preparing native dependencies
✔ Packaging Application
Making for the following targets: zip
✔ Making for target: zip - On platform: darwin - For arch: x64Electron Forge は、
outフォルダを作成してそこにパッケージを配置します。// macOS の例
out/
├── out/make/zip/darwin/x64/my-electron-app-darwin-x64-1.0.0.zip
├── ...
└── out/my-electron-app-darwin-x64/my-electron-app.app/Contents/MacOS/my-electron-app